ジストロフィン遺伝子のmRNA前駆体のエクソン53部分に結合することでエクソン53をスキップさせ、機能するジストロフィンタンパクを発現させるアンチセンス核酸医薬品技術及びデュシェンヌ型筋ジストロフィー治療薬を巡り、競合する日本新薬とSarepta Therapeutics社(以下「サレプタ社」)の間で特許紛争が米国で勃発しました。
アンチセンス核酸医薬品であるデュシェンヌ型筋ジストロフィー治療薬として、日本新薬は、ビルトラルセン(viltolarsen)を有効成分とするビルテプソ®(Viltepso®)を販売しており、サレプタ社は、golodirsenを有効成分とするVyondys 53®を販売しています。
デュシェンヌ型筋ジストロフィー治療薬で競合する日本新薬とセレプタ社との間で、互いの製品が、それぞれが保有するアンチセンス核酸医薬品技術に関連する特許権に対して問題を抱えている構図となっているようです。
サレプタ社が日本新薬のアンチセンス核酸医薬品技術関連米国特許に対してIPR請求(2021年6月21日)、日本新薬がサレプタ社に対して3つの訴訟を米国にて提起(2021年7月13日)、と約3週間という短期間で事態が進んだことから、水面下では両社でライセンス/和解交渉が進められていたのではないか(結局決裂した)と想像されます。
本記事では、
- 日本新薬のビルトラルセンを有効成分とするビルテプソ®とその米国特許
- サレプタ社のgolodirsenを有効成分とするVyondys 53®とその米国特許
- サレプタ社がIPR請求を行った日本新薬のアンチセンス核酸医薬品技術関連特許
- 日本新薬がサレプタ社に対して提起した訴訟(日本新薬のプレスリリース)
を眺めます。
1.日本新薬のビルテプソ®(Viltepso®)と米国保護特許
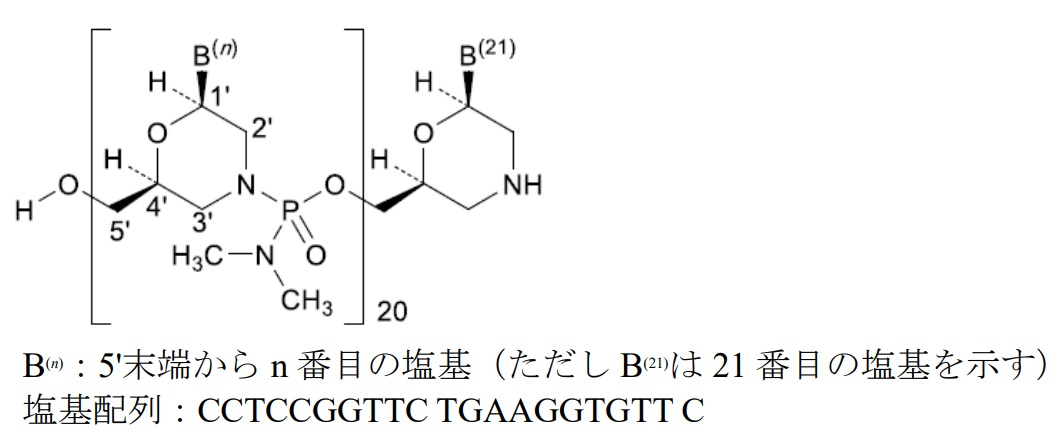 ビルテプソ®(Viltepso®)は、ビルトラルセン(viltolarsen)を有効成分とする注射剤であり、デュシェンヌ型筋ジストロフィー治療を目的として日本新薬と国立精神・神経医療研究センターで共同創製し、日本新薬で開発したモルホリノ構造を有するアンチセンス核酸です。
ビルテプソ®(Viltepso®)は、ビルトラルセン(viltolarsen)を有効成分とする注射剤であり、デュシェンヌ型筋ジストロフィー治療を目的として日本新薬と国立精神・神経医療研究センターで共同創製し、日本新薬で開発したモルホリノ構造を有するアンチセンス核酸です。
ビルトラルセンは、ジストロフィン遺伝子のmRNA前駆体のエクソン53部分に結合することでエクソン53をスキップさせ、機能するジストロフィンタンパクを発現させます。
2020年3月25日に「エクソン53スキッピングにより治療可能なジストロフィン遺伝子の欠失が確認されているデュシェンヌ型筋ジストロフィー」を効能・効果として国内で承認されました。米国では、2020年8月12日に承認されました。
Viltepso®のOrange bookには、2つの米国特許(9,079,934および10,870,676。現時点ではいずれも2031年8月31日に満了。)が掲載されています。特許9,079,934については存続期間延長手続きがされており、認められれば2034年8月12日が満了日となる見込みです。
| Patent No. | Assignee | Claim 1 | Memo. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9,079,934 | NIPPON SHINYAKU CO., LTD. NATIONAL CENTER OF NEUROLOGY AND PSYCHIATRY | An antisense oligomer which causes skipping of the 53rd exon in the human dystrophin gene, consisting of the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 35, wherein the antisense oligomer is an oligonucleotide having the sugar moiety and/or the phosphate-binding region of at least one nucleotide constituting the oligonucleotide modified, or a morpholino oligomer. | Patent term extension application under 35 USC 156 was filed. |
| 10,870,676 | NIPPON SHINYAKU CO., LTD. NATIONAL CENTER OF NEUROLOGY AND PSYCHIATRY | A method of treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in a patient in need thereof comprising administering an antisense oligomer, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or hydrate thereof, wherein the antisense oligomer consists of a nucleotide sequence complementary to the sequence consisting of the 36th to the 56th nucleotides from the 5′ end of the 53rd exon in a human dystrophin pre-mRNA, and wherein the 53rd exon in the human dystrophin pre-mRNA consists of a nucleotide sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 1. | This patent is subject to a terminal disclaimer. |
2.サレプタ社のVyondys 53®(golodirsen)と米国保護特許
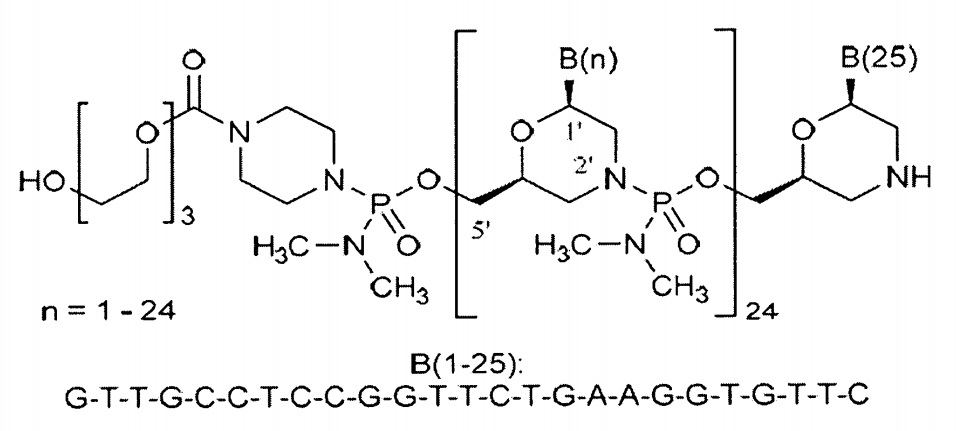 Vyondys 53®は、golodirsenを有効成分とする注射剤であり、ビルトラルセンと同種のアンチセンス核酸医薬です。2019年12月12日に、「エクソン53スキッピングにより治療可能なジストロフィン遺伝子の欠失が確認されているデュシェンヌ型筋ジストロフィー」の適応で、サレプタ社が米国で承認を取得しました。
Vyondys 53®は、golodirsenを有効成分とする注射剤であり、ビルトラルセンと同種のアンチセンス核酸医薬です。2019年12月12日に、「エクソン53スキッピングにより治療可能なジストロフィン遺伝子の欠失が確認されているデュシェンヌ型筋ジストロフィー」の適応で、サレプタ社が米国で承認を取得しました。
Vyondys 53®のOrange bookには、10件の米国特許が掲載されています。The University of Western Australiaが特許権者である特許9,024,007、RE47,691、9,994,851、10,227,590、10,266,827及び10,421,966については存続期間延長手続きがされており、認められる延長期間が決まれば登録させる1つが選択されると考えられます。
参考:
- 2019.12.12 Sarepta Therapeutics press release: Sarepta Therapeutics Announces FDA Approval of VYONDYS 53™ (golodirsen) Injection for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) in Patients Amenable to Skipping Exon 53
- 2013.04.11 Sarepta Therapeutics press release: Sarepta Therapeutics and University of Western Australia Announce Exclusive Worldwide Licensing Agreement for Exon-Skipping Program in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
3.サレプタ社が日本新薬のアンチセンス核酸医薬品技術関連特許にIPR請求
サレプタ社は、2021年6月21日に、日本新薬及び国立精神・神経医療研究センターが保有する以下の7つのアンチセンス核酸医薬品技術関連特許に対して無効審判請求(IPR請求)を行いました(参考)。
| CASE No. | Patent No. | Claim1 |
|---|---|---|
| IPR2021-01134 | 9,708,361 | An antisense oligomer which causes skipping of the 53rd exon in the human dystrophin gene, consisting of the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 57, wherein the antisense oligomer is an oligonucleotide in which the sugar moiety and/or the phosphate-binding region of at least one nucleotide constituting the oligonucleotide is modified, or a morpholino oligomer. |
| IPR2021-01135 | 10,385,092 | A phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) antisense oligomer that causes skipping of the 53rd exon in a human dystrophin pre-mRNA, consisting of a 25-mer oligomer that is 100% complementary to the 36th to the 60th nucleotides from the 5′ end of the 53rd exon in said human dystrophin pre-mRNA, wherein the 53rd exon in said human dystrophin pre-mRNA consists of a nucleotide sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 1, and wherein said PMO antisense oligomer hybridizes to said pre-mRNA with Watson-Crick base pairing under physiological conditions. |
| IPR2021-01136 | 10,407,461 | A phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) antisense oligomer that causes skipping of the 53rd exon in a human dystrophin pre-mRNA, consisting of a 25-mer oligomer that is 100% complementary to the target sequence 5′-GAACACCUUCAGAACCGGAGGCAAC-3′ (SEQ ID NO: 124) of said human dystrophin pre-mRNA, wherein said PMO antisense oligomer hybridizes to said target sequence with Watson-Crick base pairing under physiological conditions, wherein each phosphorodiamidate morpholino monomer of said PMO antisense oligomer has the formula: ##STR00024## wherein each of R2 and R3 represents a methyl; and wherein Base is a nucleobase selected from the group consisting of uracil, cytosine, thymine, adenine, and guanine. |
| IPR2021-01137 | 10,487,106 | A phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) consisting of a 25-mer antisense oligomer that is 100% complementary, according to Watson-Crick base pairing, to the 36th to the 60th nucleotides from the 5′ end of the 53rd exon in a human dystrophin pre-mRNA, wherein the 53rd exon in said human dystrophin pre-mRNA consists of a nucleotide sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein each phosphorodiamidate morpholino monomer of said PMO has the formula: ##STR00024## wherein each of R2 and R3 represents a methyl; wherein Base is a nucleobase selected from the group consisting of cytosine, thymine, adenine, and guanine, and wherein the 5′ end of said PMO has a formula selected from the group consisting of: ##STR00025## |
| IPR2021-01138 | 10,647,741 | A method comprising administering to a patient with DMD an antisense phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) consisting of a 25-mer oligomer that is 100% complementary to the 36th to the 60th nucleotides from the 5′ end of the 53rd exon in a human dystrophin pre-mRNA, wherein the 53rd exon in said human dystrophin pre-mRNA consists of a nucleotide sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein said PMO hybridizes to said human dystrophin pre-mRNA with Watson-Crick base pairing, and wherein skipping of the 53rd exon is induced in said patient. |
| IPR2021-01139 | 10,662,217 | A method of treating a DMD patient comprising intravenously administering to said patient an oligomer comprising: a) a phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) that is 100% complementary to the 36th to the 60th nucleotides from the 5′ end of the 53rd exon in a human dystrophin pre-mRNA, wherein the 53rd exon in said human dystrophin pre-mRNA consists of a nucleotide sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein said PMO hybridizes to said human dystrophin pre-mRNA with Watson-Crick base pairing, wherein the phosphorodiamidate morpholino monomers of said PMO have the formula: ##STR00024## wherein each of R2 and R3 represents a methyl; and wherein Base is a nucleobase selected from the group consisting of: uracil, cytosine, thymine, adenine, and guanine; and b) a group at the 5′ end of said PMO with the formula: ##STR00025## |
| IPR2021-01140 | 10,683,322 | A solid-phase method of making an oligomer comprising a phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) and a group at the 5′ end of said PMO, wherein said PMO is 100% complementary to the 36th to the 60th nucleotides from the 5′ end of the 53rd exon in a human dystrophin pre-mRNA, wherein the 53rd exon in said human dystrophin pre-mRNA consists of a nucleotide sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein said PMO hybridizes to said human dystrophin pre-mRNA with Watson-Crick base pairing, wherein the phosphorodiamidate morpholino monomers of said PMO have the formula: ##STR00024## wherein each of R2 and R3 represents a methyl; wherein Base is a nucleobase selected from the group consisting of: uracil, cytosine, thymine, adenine, and guanine; and wherein the group at the 5′ end of said PMO has the formula: ##STR00025## said method comprising: a) providing Compound 1: ##STR00026## wherein T represents trityl, monomethoxytrityl, or dimethoxytrityl; wherein each of R2 and R3 represents a methyl; and wherein B.sup.P is a protected Base, b) reacting said Compound 1 with an acid to form Compound 2; ##STR00027## c) reacting said Compound 2 with a morpholino monomer in the presence of a base and a solvent; d) repeating steps b) and c) until Compound 3 is complete; ##STR00028## e) reacting said Compound 3 with a deprotecting agent to form Compound 4; and ##STR00029## f) reacting Compound 4 with an acid to form said oligomer. |
4.日本新薬がサレプタ社に対して特許権侵害訴訟を提起
日本新薬の2021年7月14日付プレスリリース「サレプタ社に対する訴訟の提起について」によると、日本新薬は、サレプタ社に対し、日本新薬の知的財産を防御する目的でデラウェア州連邦地方裁判所 (デラウェア州ウィルミントン)に3つの訴訟を提起したとのことです。同プレスリリースによれば、3つの訴訟の概要は以下のとおり。
- 日本新薬は、サレプタ社が行った日本新薬アンチセンス核酸医薬品技術関連特許の無効審判請求(IPR請求)に対して仮差止命令申請を行った。
- 日本新薬は、サレプタ社がThe University of Western Australiaから取得した特許は無効であり、ビルテプソ®はその特許を侵害していないことの確認を求める訴訟を提起した。ビルテプソ®を発見したのは日本新薬とその共同研究先の研究者であり、その発見はサレプタ社の知的財産には依存していない。
- 日本新薬の特許にはVYONDYS 53®の塩基配列が含まれることから、サレプタ社のデュシェンヌ型筋ジストロフィー治療薬であるVYONDYS 53®に対する特許侵害訴訟も提起した。
参考:
- 2021.07.14 日本新薬 press release: 「サレプタ社に対する訴訟の提起について」
- Nippon Shinyaku.,Ltd. v. Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc.(Filed: July 13, 2021; Case No.: 1:2021cv01015)

コメント
【続報】
日本新薬にとって朗報。地裁判決をCAFCが覆す。
U.S. biotech Sarepta loses bid to challenge rival’s muscular dystrophy patents
https://www.reuters.com/legal/transactional/us-biotech-sarepta-loses-bid-challenge-rivals-muscular-dystrophy-patents-2022-02-08/
Nippon Shinyaku Co v. Sarepta Therapeutics Inc, U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit, No. 21-2369
https://cafc.uscourts.gov/opinions-orders/21-2369.OPINION.2-8-2022_1904898.pdf
【メモ】
Sarepta 2022 Annual report FORM 10-K (2023.2.28)
https://investorrelations.sarepta.com/static-files/03e9eabb-9ec5-4d9b-82d1-28b2ec57010c
On July 13, 2021, Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd. (“Nippon Shinyaku” or “NS”) filed a lawsuit against the Company in the U.S. District Court for the District of Delaware.
NS asserts a claim for breach of contract arising from Sarepta filing seven petitions for Inter Partes Review (“IPR Petitions”) with the Patent Trial and Appeal Board at the USPTO (PTAB Case Nos. IPR2021-01134, IPR2021-01135, IPR2021-01136, IPR2021-01137, IPR2021-01138, IPR2021-01139, IPR2021-01140) in which Sarepta sought to invalidate certain NS patents concerning exon 53 skipping technology (U.S.Patent Nos. 9,708,361, 10,385,092, 10,407,461, 10,487,106, 10,647,741, 10,662,217, and 10,683,322, respectively, and collectively the “NS Patents”).
In addition, NS asserts claims for patent infringement and willful infringement of each of the NS Patents allegedly arising from Sarepta’s activities, including the sale of, its exon 53 skipping product, VYONDYS 53 (golodirsen). NS further seeks a determination of noninfringement by NS alleged to arise from NS’s activities, including the sale of, its exon 53 skipping product, Viltepso (viltolarsen) and invalidity of certain patents licensed to the Company from University of Western Australia (“UWA”) (U.S. Patent Nos. 9,994,851, 10,227,590, and 10,266,827, collectively the “UWA Patents”).
NS is seeking legal fees and costs, an unspecified amount of monetary relief (treble damages) attributed to Sarepta’s alleged infringement, and such other relief as the court deems just and proper.
In January 2022, the PTAB granted institution of all claims of all NS Patents in response to Sarepta’s IPR Petitions and determined that Sarepta has demonstrated a reasonable likelihood of success in proving that the NS Patents are unpatentable.
NS filed a motion for preliminary injunction solely seeking Sarepta’s withdrawal of the IPR Petitions, which was ultimately granted after the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit reversed and remanded to the district court on February 8, 2022.
Sarepta subsequently withdrew the IPRs, which were terminated on June 14, 2022.
On December 27, 2021, the district court partially granted and denied the motion to dismiss by Sarepta and ordered NS to file a Second Amended Complaint (“SAC”), which it did on January 14, 2022.
In the SAC, NS maintains all claims of the original complaint of July 13, 2021, except a determination of non-infringement of the UWA Patents.
On January 28, 2022, Sarepta filed its answer to the SAC, with defenses and counterclaims against NS and NS Pharma Inc. that include infringement of the UWA Patents allegedly arising from their activities concerning, including the sale of, its exon 53 skipping product, Viltepso (viltolarsen) and breach of contract.
Sarepta is also seeking a determination of invalidity of the NS Patents.
Sarepta is seeking an award of relief in its defenses to NS’ allegations, a judgment of breach of contract, a determination of invalidity of the NS Patents, a judgment of infringement and willful infringement of the UWA Patents, legal fees and costs, an unspecified amount of monetary relief (treble damages) attributable to NS’ alleged infringement, and such other relief as the court deems just and proper.
The Court entered a scheduling order with a trial scheduled to commence on May 13, 2024.
Sarepta 2024.05.01 SEC filing 10-Q Quarterly report
https://investorrelations.sarepta.com/static-files/108a1d0f-5407-4fd5-b212-fdc273c12608
米国では複雑な裁判経過をたどっているが、日本でも訴訟が進行中のようです。
“On or about June 5, 2023, Sarepta initiated a patent infringement lawsuit against Nippon Shinyaku in Japan, alleging that NS’s production, sales and offers to sell Viltepso infringe Sarepta’s Japanese Patent No. 6406782. NS filed its preliminary answer on July 13, 2023. A final hearing is set for July 25, 2024.”
Sarepta社の日本特許6406782
【請求項1】
ヒトジストロフィン遺伝子のエキソン53に対して100%相補的な塩基配列を含む21塩基のアンチセンスオリゴヌクレオチドであって、該塩基配列は、配列番号431の19個の連続する塩基を含み、該アンチセンスオリゴヌクレオチドは、モルフォリノアンチセンスオリゴヌクレオチドであり、該アンチセンスオリゴヌクレオチドは、エキソン53スキッピングを誘導する、アンチセンスオリゴヌクレオチドまたは薬学的に受容可能なその塩。